Abstract
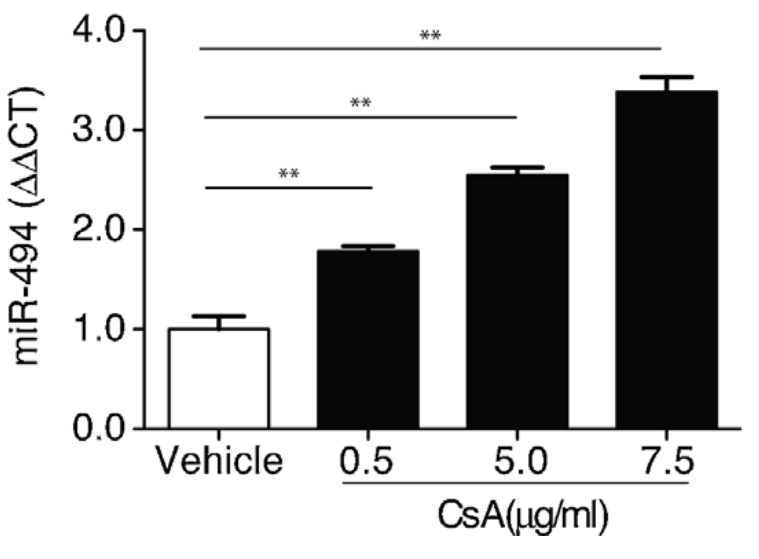
A major complication associated with cyclosporine (CsA) treatment is nephrotoxicity. In this study, we examined whether microRNAs play a role in cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity. Treatment of mice with CsA resulted in nephrotoxicity that was associated with an early increase in expression of microRNA mmu-miR-494 (miR-494). Similarly, tubular epithelial cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by CsA toxicity resulted in the upregulation of microRNA-494 and a decrease in PTEN levels in vitro. miR-494 directly targeted Pten and negatively regulated its expression. Preventing Pten targeting by miR-494 was sufficient to prevent CsA induced EMT. Knockdown of miR-494 prevented the downregulation of PTEN in tubular epithelial cells following CsA treatment and also prevented CsA induced EMT. Thus, miR-494 plays a major role in promoting CsA induced nephrotoxicity through its ability to target Pten thereby contributing to EMT. We suggest that manipulating miR-494 expression may represent a novel approach to preventing EMT associated with CsA induced nephrotoxicity.
* corresponding author